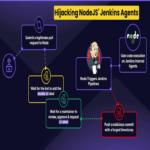
Emerging Threats from Generative AI Misuse: A Technical Analysis
The rapid advancement of generative artificial intelligence (AI) technologies has introduced new vectors for cyber threats, fundamentally altering the cybersecurity landscape. As these systems become more sophisticated, malicious actors are increasingly weaponizing them to conduct attacks with unprecedented scale and efficiency.
Technical Mechanisms of AI-Powered Threats
Generative AI models, particularly large language models (LLMs) and diffusion models, can be misused in several technically sophisticated ways:
- Automated phishing campaigns: AI can generate highly personalized phishing emails at scale, bypassing traditional spam filters through natural language variations.
- Deepfake engineering: Voice cloning and video synthesis technologies enable sophisticated social engineering attacks.
- Malware development: AI-assisted code generation lowers the barrier for creating polymorphic malware that evades signature-based detection.
- Credential stuffing optimization: AI can analyze breached credential databases to predict likely password combinations.
Key Vulnerabilities Exploited
The misuse of generative AI primarily targets fundamental security weaknesses:
- Human factors in authentication systems
- Limitations of pattern-matching security solutions
- Latency in threat intelligence updates
- Insufficient behavioral analysis capabilities in legacy systems
Defensive Countermeasures
To combat AI-powered threats, security professionals must implement multi-layered technical defenses:
- Behavioral analytics: Deploy machine learning systems that analyze user behavior patterns rather than static signatures.
- Content verification protocols: Implement cryptographic signing for official communications to combat deepfakes.
- Adversarial training: Security AI systems should be trained against known attack patterns generated by malicious AI.
- Zero-trust architectures: Enforce strict access controls regardless of communication authenticity.
Future Threat Landscape
As generative AI capabilities evolve, we anticipate several emerging technical challenges:
- Automated vulnerability discovery and exploitation at scale
- AI-driven social engineering that adapts in real-time to countermeasures
- Synthetic identity creation for long-term infiltration
- AI-coordinated distributed attacks across multiple vectors simultaneously
The cybersecurity community must prioritize research into AI-specific defense mechanisms while advocating for responsible AI development frameworks. Continuous monitoring of emerging AI capabilities is essential to stay ahead of potential misuse scenarios.
For more information on this evolving threat landscape, refer to the original source.